Introduction
___
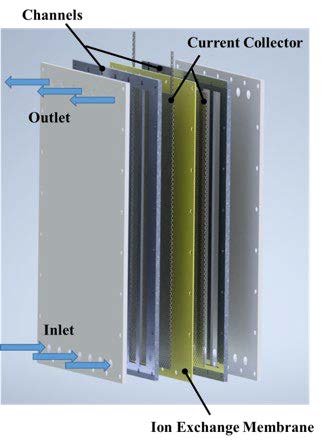
Flow electrode system, which mainly consists of flow particle electrodes, current collectors and ion exchange membrane, is a novel electrochemical technology to treat wastewater with high and/or low solution conductivity. Organic pollutants can be oxidized and reduced at the surface of particle electrodes into carbon dioxide and water, which can significantly enhance the removal rates. In addition, flow electrode system also can be applied to the removal of ammonia-nitrogen and the recovery of heavy metal ions.
Competitive advantages
___
-
Low-cost, viable alternative for resource recovery (e.g., ammonia, phosphorous and rare earth elements) from waste streams;
-
The use of flowable materials allows for the easy management of the electrode and continuous operation of the system.
Recent research projects
___
-
Flow-electrode CDI and its applications for high strength brine desalination
-
Recovery of nitrogen and phosphorus from wastewaters by integrated flow electrode/membrane systems
-
Neodymium recovery from acid mine drainage by redox flow battery desalination
Research needs
___
-
Scale-up to pilot scale operation
-
Validation of efficacy on real wastewaters
Facilities and infrastructure
___
-
UNSW Water Research Centre and UNSW CTET has extensive research resources and access to facilities including laser cutters, CNC mills, and electrochemical work stations
-
UNSW CTET has active collaboration with industry partners in Yixing capable of prototype construction